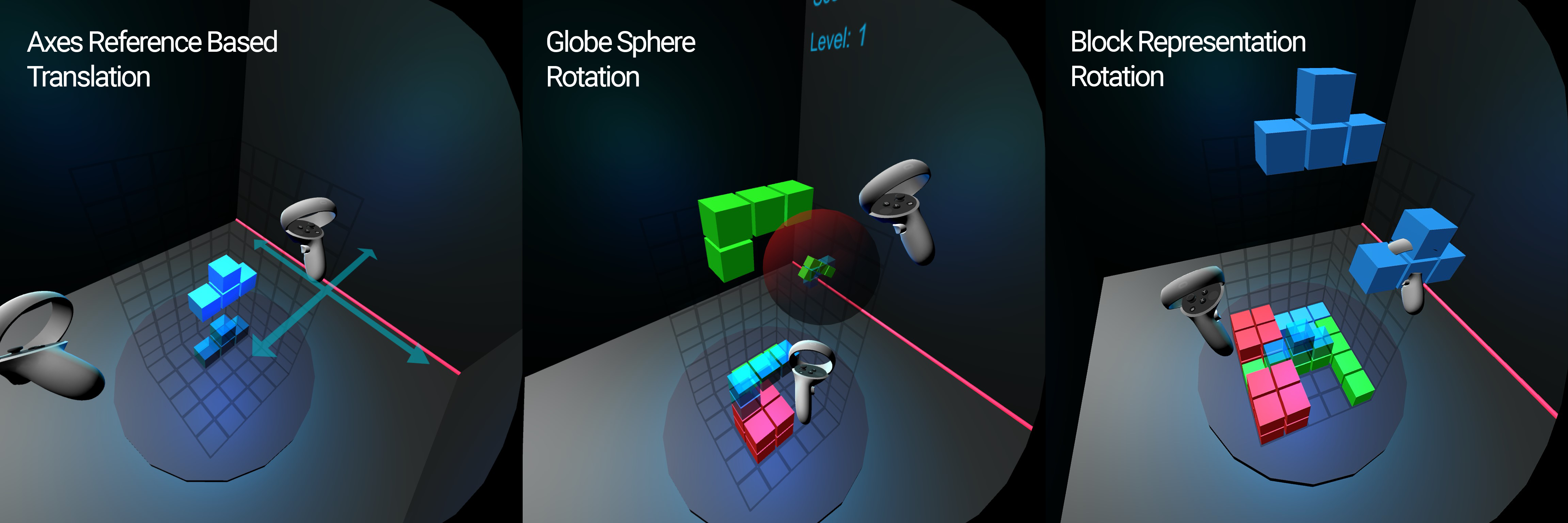
3D VR Tetris
Summary - Whether you know Tetris or not, it doesn't take much to get the gist of this true game classic. That's why its a perfect match for a gamified test environment for various interaction and manipulation techniques in virtual reality.
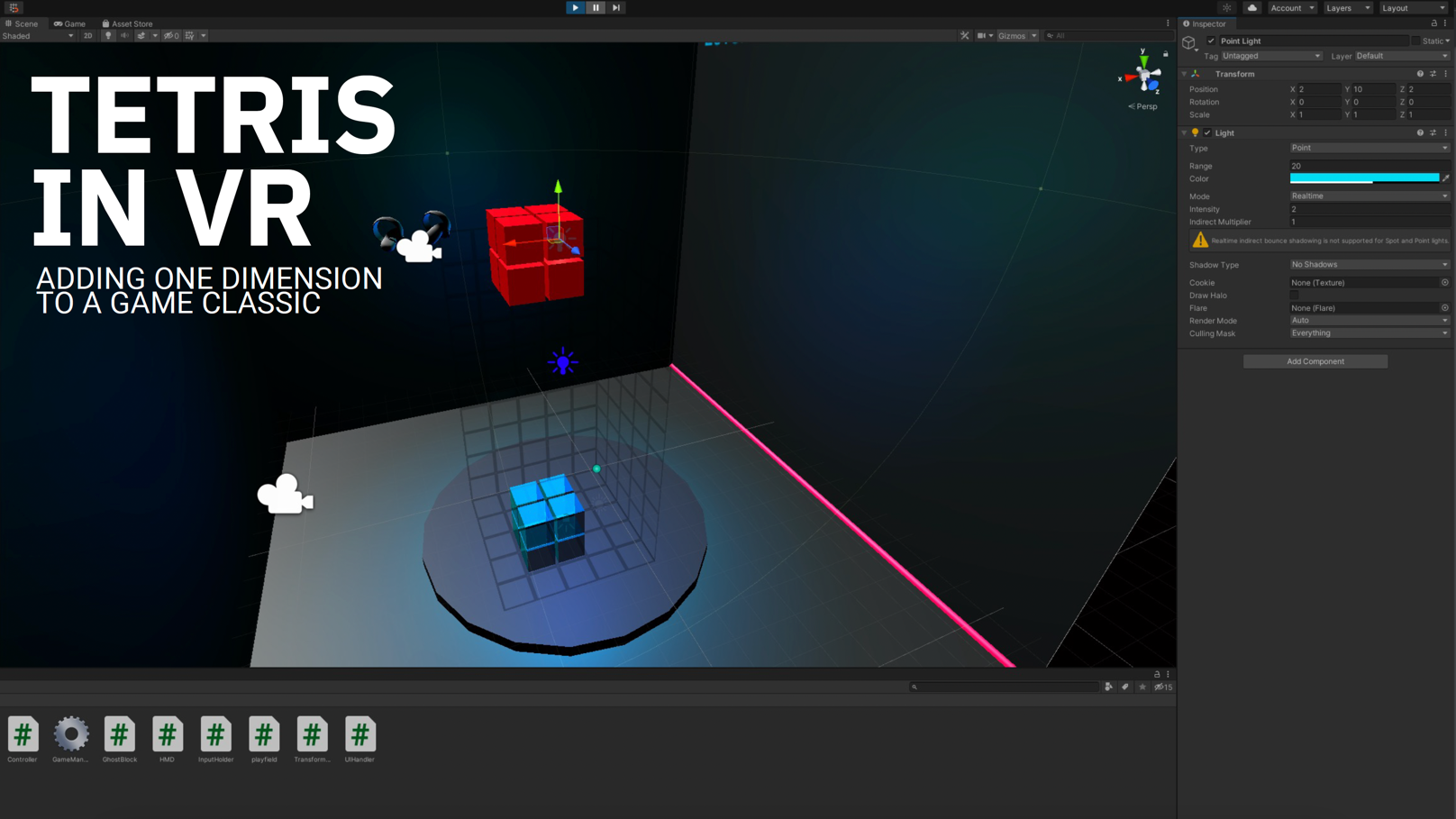
3D VR Tetris offers an entertaining and easily understandable task for a scientific user research in virtual reality and spatial computing. Our prorotype offers the barebone functionality to implement interactions methods and quantitative measurements.
Besides, adding one dimension to Tetris makes the game much more fun and exceptionally harder to play.
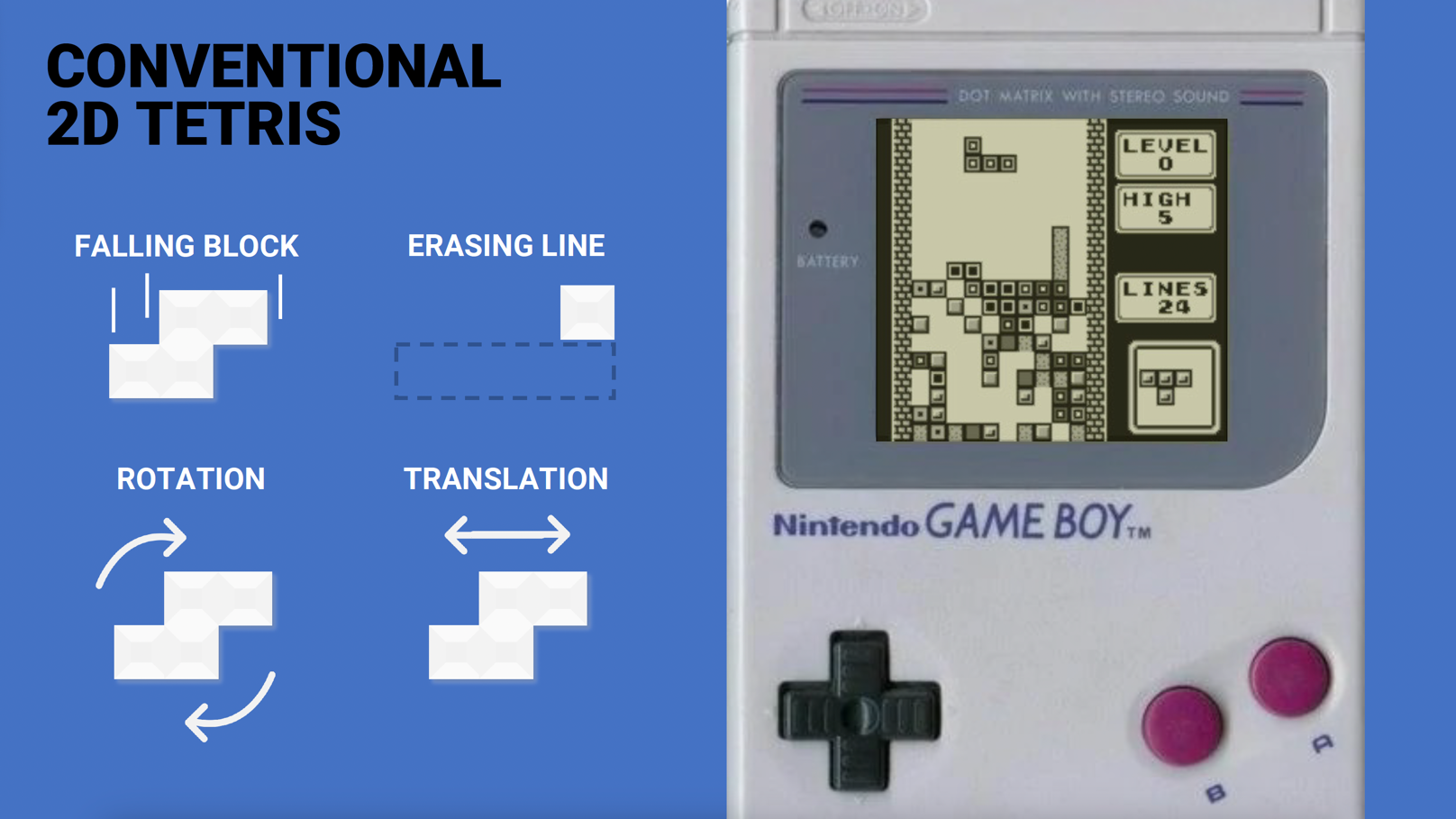
Conventional Tetris
Conventional 2D Tetris offers little freedom in the way objects can be moved. Tetris players can only move and rotate blocks along one axis, therefore they have 1 Degree of Freedom (DoF).
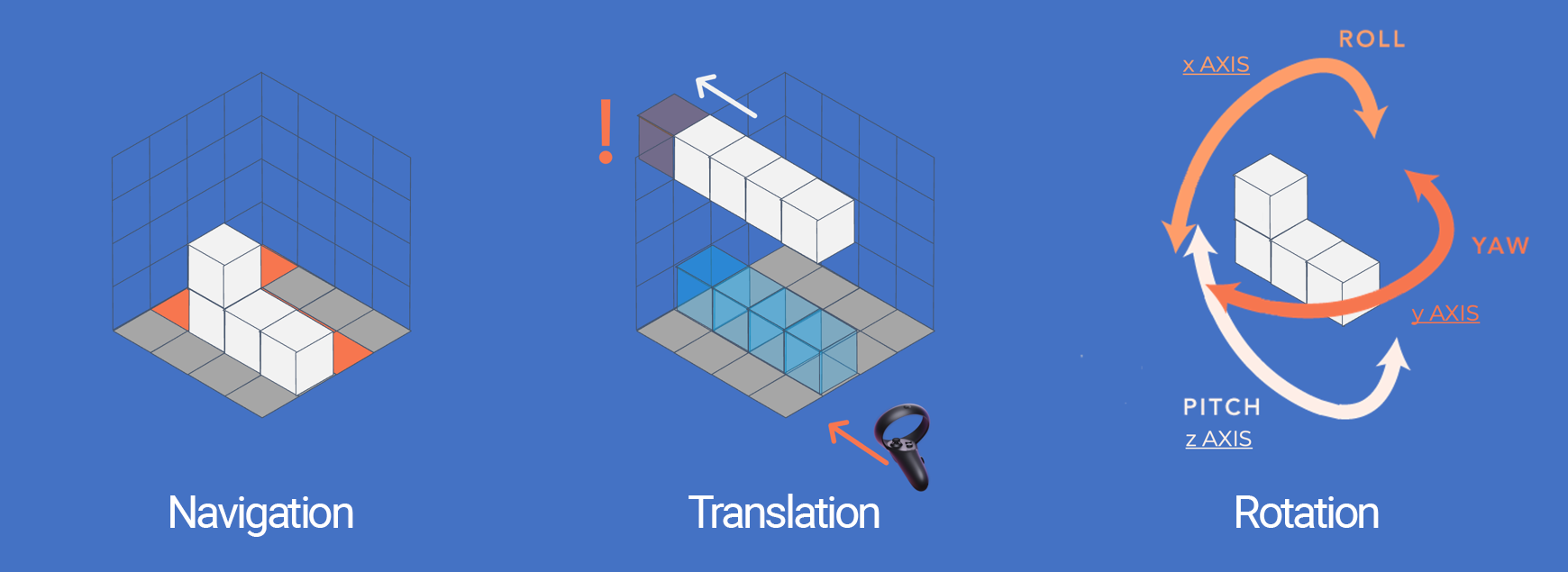
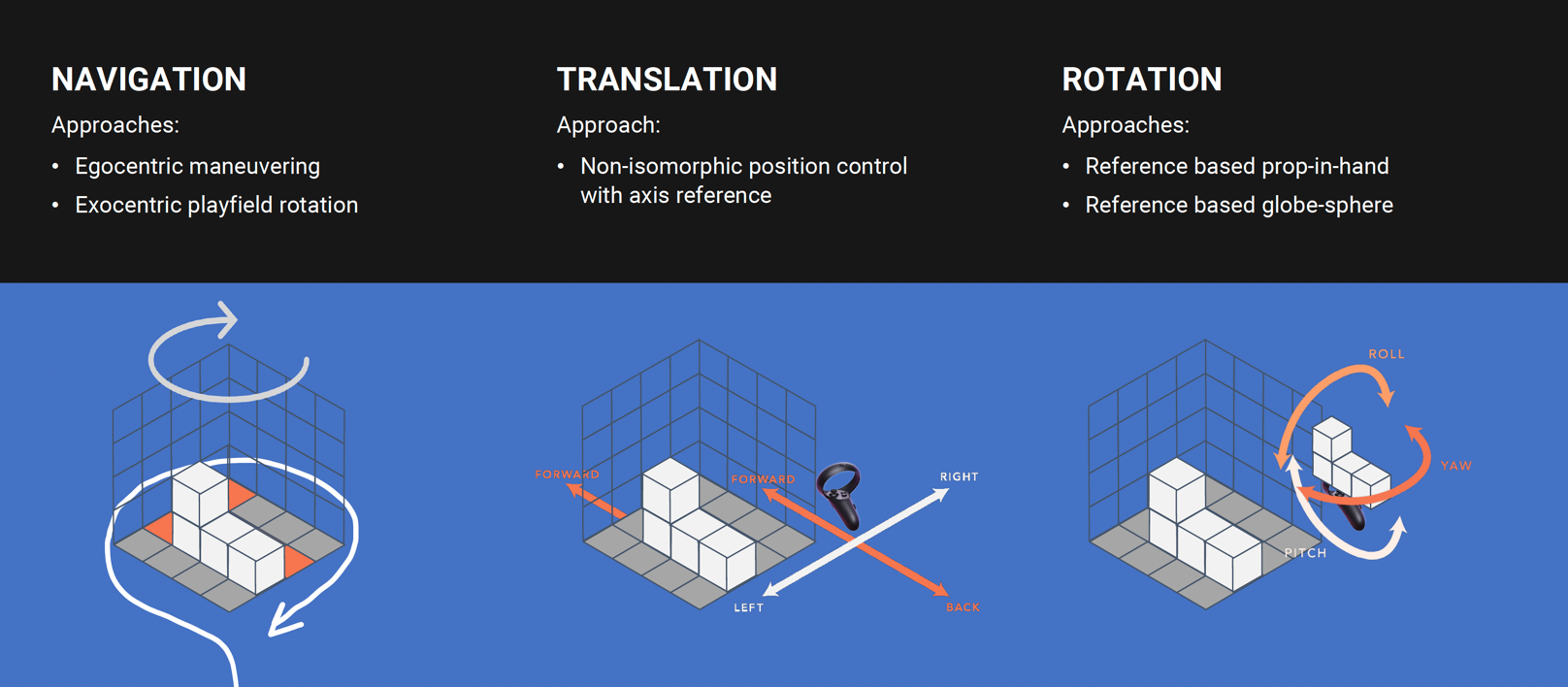
3D Interaction (Navigation / Translation / Orientation)
Extending Tetris by a thrid dimension offers new interaction possibilities:
- The player can move around the playing field or the playing field can be moved (rotated)
- Falling blocks can be translated along two axes (2 DoF.)
- Falling blocks can be rotated along three axes (3 DoF.)
Interaction Challenges
Three dimensions also include certainc challenges to the interaction such as:
- Navigational challenges and occlusion due to falling blocks
- Limited interaction space and translational challenges due to gain in freedom of block movement
- Going from 1 DoF. to 3 DoF. drastically increases the complexity of block rotation
Interaction Design
This project approached multiple solutions for interacting with complex 3D objects in space. First investigations led to the adaption of the following techniques:
- Exocentric playfield rotation over egocentric maneuvering
- Non-isomorphic position control of the falling block
- Reference based rotation either with in-hand block reference or globe-sphere representation
The pictures below depict exemplary scenes and interaction techniques from our pilot study with VR Tetris